Plasma Therapy Applications in Dermatology with Emphasis on CAP (Cold Atmospheric Plasma) and Electro-Surgical, Fractional Plasma
Definition of Plasma and Plasma Therapy Principles
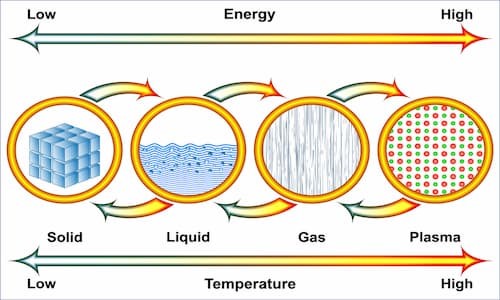
Plasma, as the fourth state of matter, is a combination of ionized gases made up of positive ions, free electrons, and neutral molecules. Due to its ionized nature, plasma behaves differently from ordinary gas. Unlike gas, where molecules are neutral, in plasma, charged particles are influenced by electric and magnetic fields and react intensely. These characteristics have led to plasma having widespread applications in various industries, including medicine.
Plasma therapy is one of the advanced medical technologies where electrical energy is used to ionize a gas and produce plasma. This technology is divided into two main categories:
- Cold Plasma (Cold Atmospheric Plasma – CAP): Produced at low temperatures (around room temperature) and used for non-invasive treatments, especially on the skin’s surface.
- Thermal Plasma: Has a higher temperature and is used for deeper treatments, such as skin rejuvenation and removal of skin lesions.
- Fractional Plasma Technology – A New Generation of Plasma Therapy: Fractional plasma is a combination of plasma technology and fractional techniques (dividing energy into smaller points), which allows for uniform and precise treatment.
Plasma therapy, due to its ability to create controlled changes in tissues, is recognized as a non-invasive and effective method in dermatology and aesthetics. It is widely used to treat various skin conditions, including wounds, wrinkles, and skin sagging.
A. Cold Plasma (CAP) and Its Applications in Medicine
Characteristics of Cold Plasma:
-
Low Temperature and Its Effects on Living Tissues:
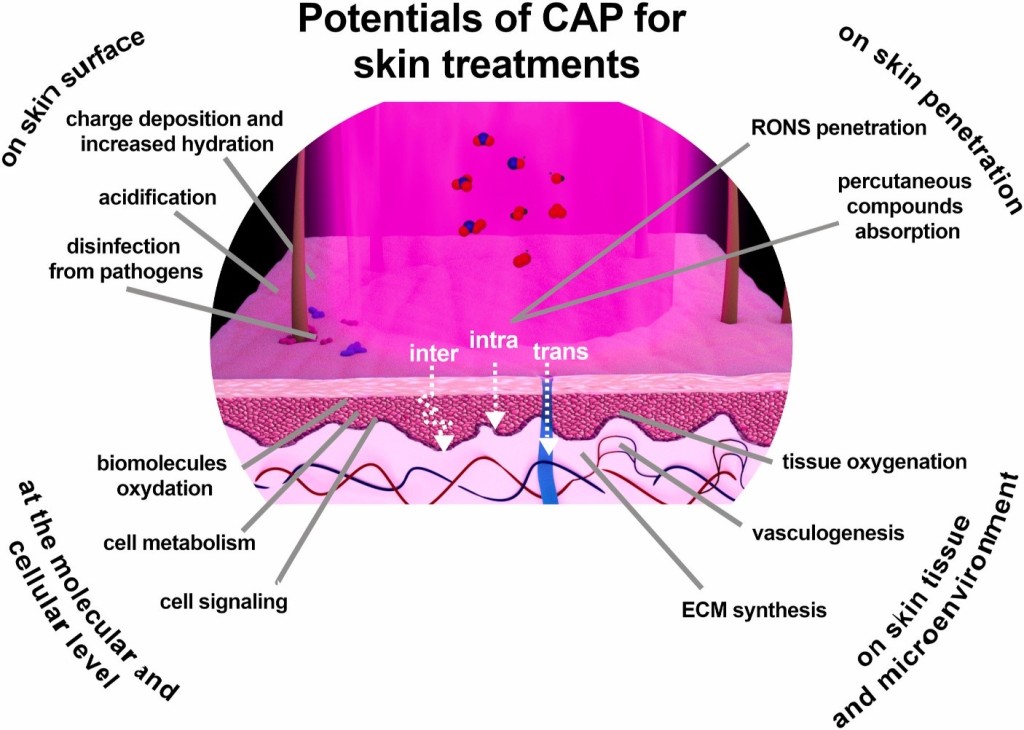
Cold plasma, due to its low temperature (below 40°C), is recognized as a non-invasive and safe therapeutic tool for use on living tissues. This characteristic is specifically due to the process of plasma generation at atmospheric pressure, which allows the production of active species without significantly increasing the temperature. Unlike thermal plasmas, which have very high temperatures (thousands of degrees Celsius) and can destroy healthy tissues, CAP produces energy within a temperature range close to body temperature, applying its therapeutic effects without harming healthy cells. At low temperatures, CAP can act on the skin and soft tissues without causing burns or structural damage. This feature makes CAP suitable for the treatment of skin diseases, chronic wound healing, and even applications in dentistry and ophthalmology. Furthermore, the low temperature is especially beneficial for patients with sensitive conditions (such as diabetic patients with chronic wounds) because it prevents inflammation or secondary damage. The low temperature of CAP also plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular integrity. This feature allows natural biological processes, such as cellular proliferation and tissue regeneration, to continue uninterrupted and without degradation. In fact, CAP acts as a biological stimulant, promoting natural healing processes without inducing active damage.
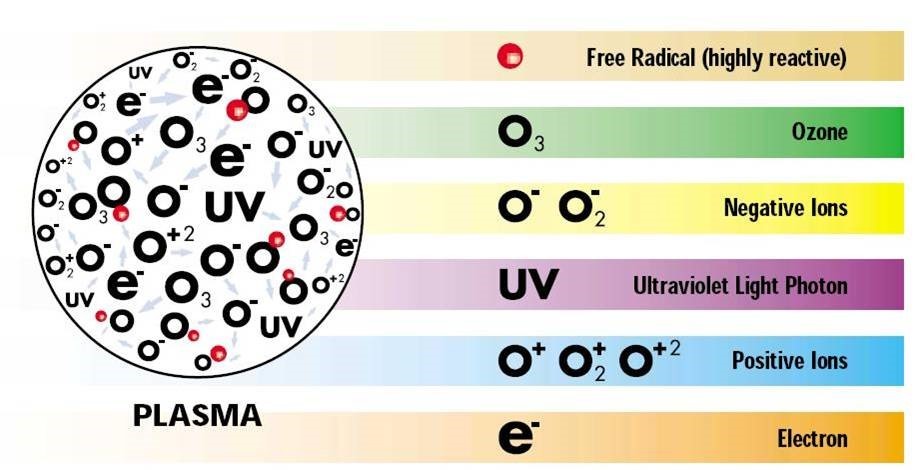
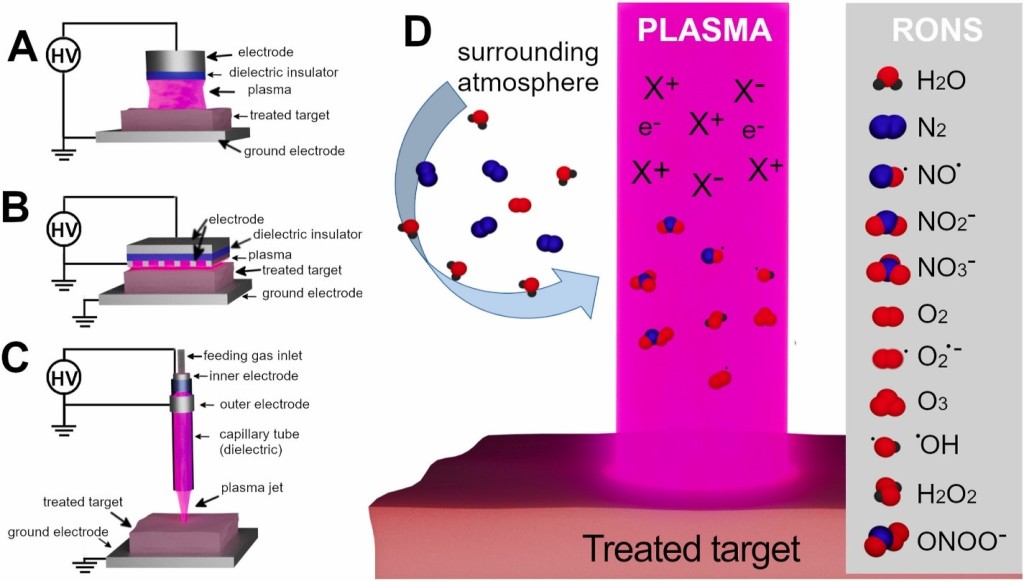
2. Production of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS):
Cold plasma is a rich source of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). These species include molecules like hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), ozone (O₃), hydroxyl radicals (OH), nitric oxide (NO), and proximities (ONOO⁻). The production of these species occurs in the plasma environment due to the ionization of gases at atmospheric pressure and plays a key role in the therapeutic effects of CAP.
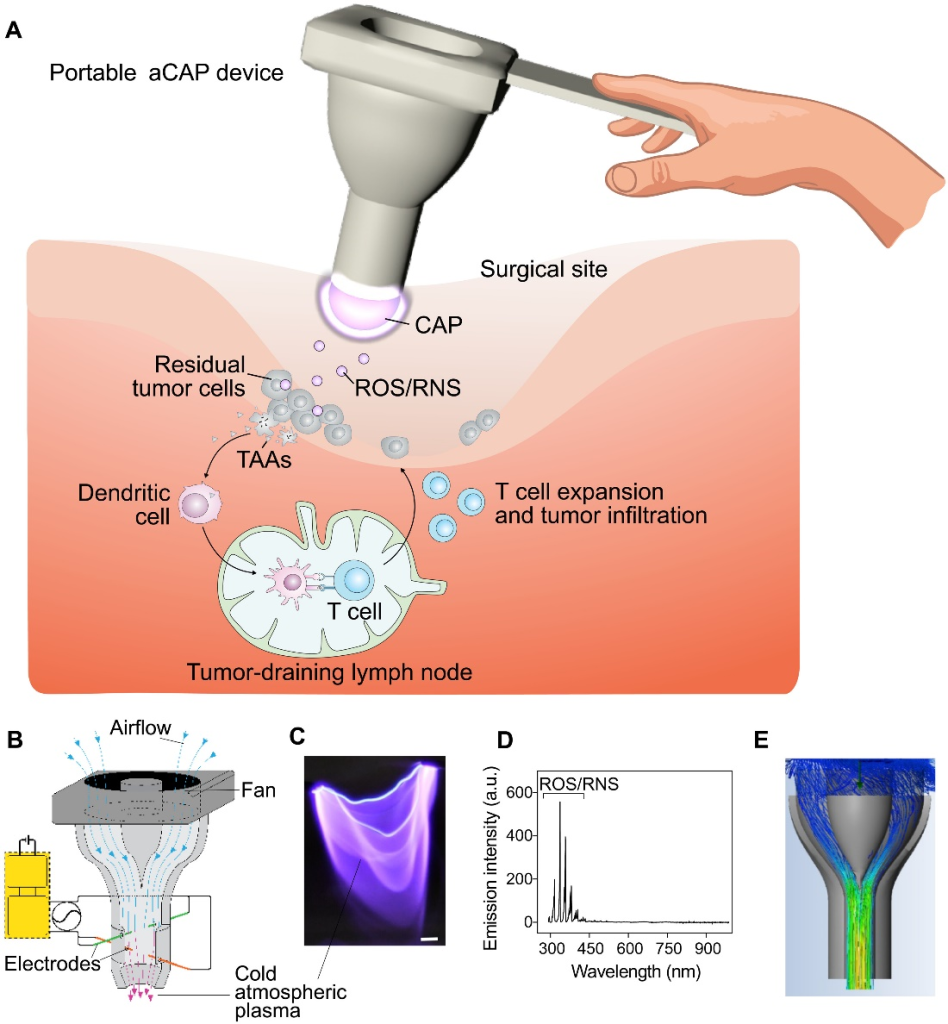
- Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS):
These molecules, due to their high reactivity, are capable of damaging the cell walls of microorganisms. For this reason, CAP has strong disinfecting properties and can kill bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This property is particularly beneficial in the treatment of infectious wounds and skin diseases that are associated with chronic infections. Additionally, ROS stimulate intracellular signaling pathways, enhancing the processes of regeneration and repair.
- Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS):
Molecules like nitric oxide (NO) play vital roles in various biological processes, including blood vessel dilation (vasodilation) and the regulation of immune responses. Nitric oxide produced by CAP can improve local blood circulation and enhance oxygen supply to damaged tissues. This feature is especially important in chronic wounds with poor blood circulation. Furthermore, RNS reduces inflammation and regulates immune responses, creating a more favorable environment for wound healing.
3.Interaction of Reactive Species with Human Cells:
The reactive species produced by cold plasma have multiple effects on human cells. These effects include the stimulation of cell proliferation, cell differentiation, and the induction of programmed cell death in damaged or cancerous cells. For example:
- Stimulation of Fibroblasts:
Fibroblasts are key cells in the tissue repair process. The reactive species produced by CAP increase fibroblast proliferation and stimulate collagen production, which helps accelerate the wound healing process.
- Induction of Cancer Cell Death:
In cancer treatment, the reactive species can induce oxidative stress and DNA damage, triggering programmed cell death in cancerous cells while not harming healthy cells.
Clinical Applications of CAP:
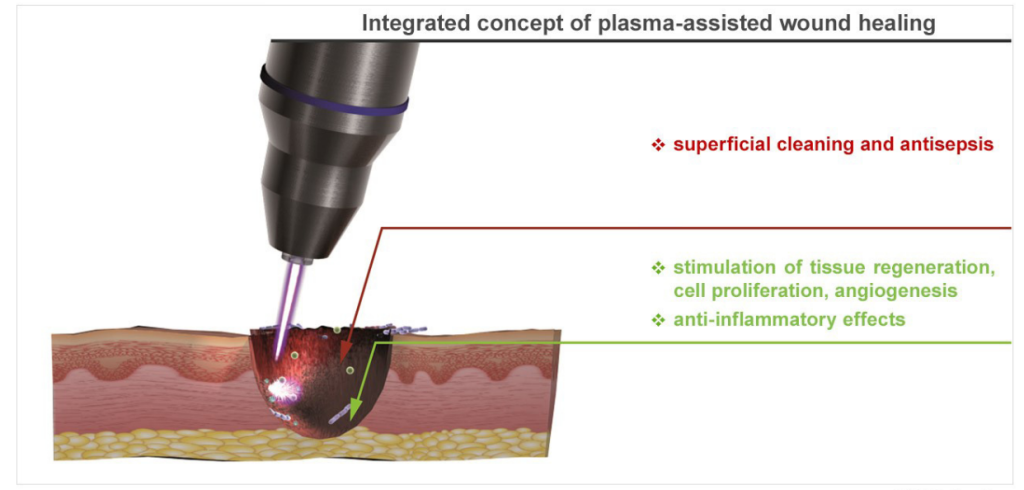
- Treatment of Chronic Wounds with Cold Plasma (CAP)
- Disinfection Effect:Cold plasma, due to the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), can eliminate bacteria, viruses, and fungi present on the surface of wounds. These reactive species penetrate the cell walls of pathogens and degrade their structures. Unlike antibiotics that may cause drug resistance, CAP effectively combats a wide range of microorganisms. This disinfecting property is particularly beneficial for the treatment of chronic wounds, such as diabetic ulcers, which are often resistant to standard treatments.
- Tissue Regeneration Stimulation:One of the key mechanisms of CAP in treating chronic wounds is the stimulation of tissue regeneration. The reactive oxygen and nitrogen species produced by cold plasma activate fibroblasts and keratinocytes around the wound. Fibroblasts play an essential role in collagen production and tissue regeneration, while keratinocytes are involved in the epithelialization process (skin surface repair). CAP increases the proliferation of these cells, thereby accelerating wound healing. Additionally, CAP enhances tissue repair by inducing controlled microtrauma, which signals further regeneration in the tissue.
- Improved Microcirculation:Cold plasma can enhance local blood flow around the wound. This process occurs through the dilation of small blood vessels (vasodilation) and the stimulation of nitric oxide (NO) production in the tissue. Increased local blood flow means better oxygen and nutrient supply to the damaged tissues, which plays a crucial role in wound healing. Improved microcirculation is especially important in diabetic wounds, which are often associated with poor circulation. This effect helps prevent tissue necrosis and the formation of new infections in the wound area.
2. Treatment of Skin Diseases: Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) is recognized as a novel therapeutic method in dermatology due to its unique characteristics, including the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). This technology plays an effective role in the treatment of a wide range of skin diseases, particularly bacterial and inflammatory infections. In addition, CAP is used for skin rejuvenation and burn healing by stimulating the processes of cellular regeneration and remodeling. The following outlines the effects of CAP in treating skin diseases and the associated biological processes in detail:
Destruction of Microbial Cell Walls: CAP, by producing reactive molecules such as hydroxyl radicals (•OH) and hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), directly attacks the cell walls and membranes of microbes. These molecules cause the oxidation of lipids and membrane proteins, thereby destroying the cellular structure of pathogens. This process is effective for various bacteria (including antibiotic-resistant bacteria), viruses, and fungi. This property of CAP is especially useful in treating skin infections such as pustular acne and infected wounds.
Control of Inflammation and Regulation of Immune Response: In addition to its antimicrobial effects, CAP regulates inflammatory pathways by producing nitric oxide (NO) and other reactive nitrogen species. Nitric oxide is a signaling molecule that can modulate local immune responses and control inflammation by reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines. This effect is particularly beneficial for treating conditions such as eczema and psoriasis, where chronic inflammation plays a key role.
3. Effect of CAP on Burn Healing and Regeneration: Burns are among the most severe skin injuries, often associated with the risk of secondary infections and prolonged healing. CAP facilitates the wound healing process from burns through multiple mechanisms:
Acceleration of Wound Healing: Cold plasma accelerates tissue regeneration by increasing the proliferation of keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Keratinocytes are key cells in the regeneration of the epidermal layer, while fibroblasts shape the new tissue structure by producing collagen. The reactive oxygen and nitrogen species produced by CAP activate signaling pathways related to the proliferation and differentiation of these cells.
Prevention of Secondary Infections: Burn wounds provide an ideal environment for bacterial growth, which can lead to dangerous infections. CAP effectively prevents the growth of microorganisms and reduces the microbial load in wounds. This property helps reduce the need for antibiotics and lowers the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Stimulation of Angiogenesis (Blood Vessel Formation): Reactive nitrogen species, such as nitric oxide, play a role in angiogenesis. Increased angiogenesis helps improve local blood circulation, delivering more oxygen and nutrients to the burn area. This is particularly important in deep burns that are associated with reduced blood supply.
4. Effects of CAP on Skin Rejuvenation: Stimulation of Collagen and Elastin Production:
Cold plasma creates controlled microtrauma on the skin surface, activating the cellular repair process and stimulating the production of collagen and elastin. These two proteins play a fundamental role in maintaining the skin’s strength and elasticity. Increased collagen production causes the skin to become thicker and firmer, reducing fine wrinkles and superficial sagging.
Increased Cellular Regeneration: CAP stimulates the proliferation of keratinocytes, aiding in the faster regeneration of the epidermal layer. This process leads to natural exfoliation and the replacement of old cells with new ones. The result of this process is younger, clearer skin with a more uniform texture.
Control of Chronic Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is one of the key factors in skin aging. CAP helps prevent premature aging by reducing inflammation and regulating immune responses, which prevents the degradation of collagen and helps maintain skin youthfulness.
5. Applications in Dentistry:
Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) in dentistry is recognized as an innovative and non-invasive technology with various applications, particularly for disinfection and aesthetic treatments. This technology works by producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), which are capable of destroying pathogens and creating chemical changes on the surface of teeth.
Disinfection of Root Canals: The root canal is an environment that, due to its complex and impermeable structure, can harbor bacterial biofilms and resistant infections. These biofilms are collections of microorganisms protected by a matrix that are highly resistant to common treatments like antibiotics and disinfecting washes. Cold plasma, by producing reactive oxygen species like hydroxyl radicals (•OH), hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), and ozone (O₃), can effectively eliminate these biofilms. These active species destroy the bacterial cell walls and disrupt their protein and genetic structure without damaging the surrounding healthy tissue.
One of the significant advantages of CAP in root canal disinfection is that, unlike chemical and mechanical methods, this process does not require penetration into complex structures. The reactive species produced can effectively penetrate all areas of the root canal and eradicate the infection. This feature reduces the risk of reinfection and increases the success rate of root canal treatments. Studies have shown that using CAP as a supplement to traditional methods significantly reduces bacterial survival, resulting in a higher success rate for root canal treatments.
Teeth Whitening: Teeth whitening using cold plasma is based on the oxidizing
properties of the reactive species it generates. In this process, reactive molecules such as hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) and hydroxyl radicals react with organic stains and pigments present on the surface of the teeth and oxidize them. These oxidative reactions break down the molecular structure of the pigments, leading to their elimination or reduction. Unlike traditional teeth whitening methods that use high concentrations of chemicals, which may cause sensitivity or damage to tooth enamel, cold plasma is considered a safer method due to its low temperature and the absence of aggressive chemicals.
Furthermore, CAP enhances the permeability of the tooth enamel, making the whitening process more efficient. The active species generated can penetrate deeper into the enamel structure and break down sub-surface pigments as well. This characteristic makes the whitening results from cold plasma more lasting and effective. Research has also shown that this method can help strengthen the enamel structure and reduce sensitivity after treatment.
In summary, the use of cold plasma in dentistry as an advanced technology not only improves the efficiency of procedures such as root canal disinfection and teeth whitening but also plays a crucial role in enhancing the safety and reducing side effects, thus advancing the quality of dental treatments.
6. Cancer Treatment:
Mechanism of Action: CAP induces programmed cell death in cancer cells through the production of ROS and RNS.
Clinical Application: It is effective in the treatment of superficial tumors, such as squamous cell carcinoma.
B. Thermal Plasma and Its Applications in Dermatology: Features and Therapeutic Effects
Thermal Plasma is one of the advanced technologies in dermatological treatments, gaining widespread use in aesthetic and regenerative fields due to its ability to generate localized heat and have deep effects on skin tissues. This type of plasma is produced at high temperatures (several hundred degrees Celsius) and targets the skin’s surface by creating an electric arc. Below, the features of thermal plasma and its mechanisms of action on skin tissues are explained in detail.
- Localized Heat Generation and Surface Tissue Destruction: Thermal plasma, by transferring controlled heat to the skin’s surface, causes the evaporation or sublimation of dead and damaged tissues. This process is specifically used to remove skin lesions such as moles, warts, and superficial keratoses. The heat transfer to the epidermal layer induces controlled microtrauma, which activates the natural repair and regeneration mechanisms of the skin. This feature of thermal plasma allows practitioners to precisely remove unwanted tissues without damaging the surrounding healthy tissues.
The heat produced by thermal plasma also plays an important role in protein coagulation and the destruction of abnormal cells. This process is especially crucial in treating benign and precancerous skin lesions. The treated tissues are naturally expelled in a few days after the procedure, and new tissue replaces them. - Generation of Electric Arc and Tissue Sublimation: In thermal plasma, an electric arc is generated between the device and the skin’s surface, ionizing the air and producing energetic plasma. This electric arc locally impacts the surface tissues and transfers its energy in the form of heat. This process leads to tissue sublimation, meaning that the surface tissues are directly converted from solid to gas without becoming liquid. This characteristic makes the treatment highly precise and controlled, ensuring that the deeper layers of the skin are not affected.Tissue sublimation, by creating thermal microchannels in the epidermis, activates processes of regeneration and collagen production. This feature plays a crucial role in non-invasive treatments such as non-surgical blepharoplasty (eyelid lifting) and skin rejuvenation.
- Safety:
Due to its deeper and localized effects, thermal plasma is used in treatments that require precise tissue destruction or stimulation of regeneration in deeper layers. This method is an ideal option for patients who wish to avoid invasive surgery. Thermal plasma treatments typically do not require general anesthesia, and patients can return to their daily activities immediately after the procedure. - Precise Control of Depth of Penetration: One of the major advantages of thermal plasma is the ability to precisely control the depth of energy penetration. This feature allows the practitioner to tailor the treatment based on the type of lesion or the patient’s skin needs. For example, in blepharoplasty treatments, the energy is adjusted so that only the surface layers of the skin are affected, while for deeper scars or wrinkles, the energy penetrates deeper layers.
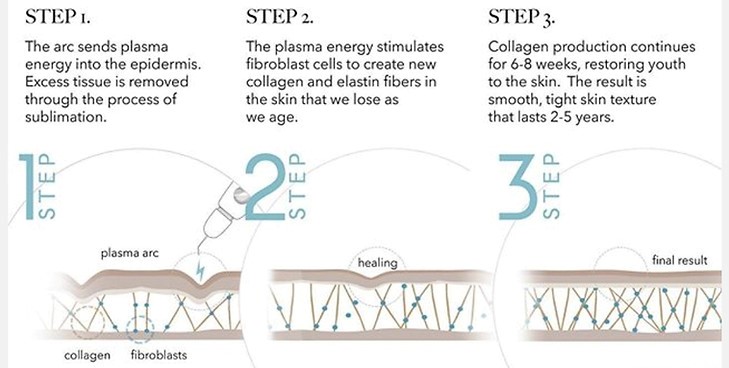
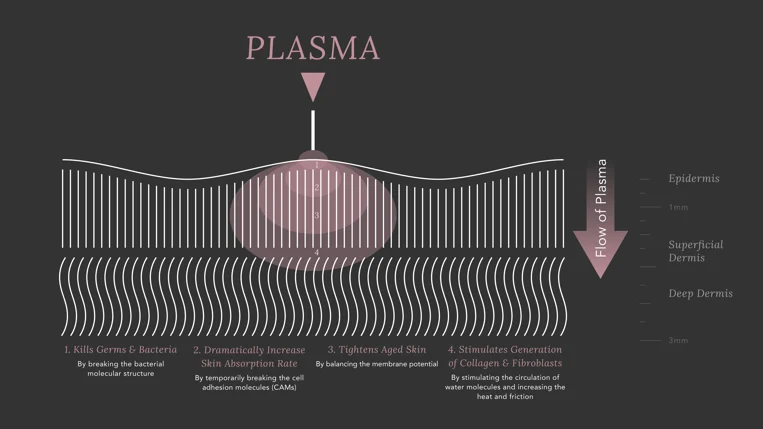
Clinical Applications of Thermal Plasma:
- Dynamic Blepharoplasty: Treatment of Eyelid Drooping Without Invasive Surgery Blepharoplasty, or eyelid surgery, is typically performed to correct cosmetic and functional issues of the eyes. While the traditional method usually requires invasive surgery and general anesthesia, dynamic blepharoplasty using thermal plasma is emerging as a non-invasive and safe option. This method is used for treating eyelid drooping, fine lines around the eyes, and puffiness under the eyes.
In dynamic blepharoplasty, thermal plasma generates electric arcs that transfer thermal energy to the skin, penetrating the superficial layers of the skin and the muscles around the eyelids. This heat stimulates collagen production and firms the skin. Additionally, the heat generated by sublimating dead cells and activating the deeper layers of the skin significantly improves skin quality and reduces sagging.
The advantages of this method over invasive surgery include faster recovery time, reduced risk of infection and bleeding, and the ability to perform the treatment in an office or clinic without the need for anesthesia. Furthermore, dynamic blepharoplasty with thermal plasma softens and enhances the elasticity of the skin around the eyes, reducing the effects of aging and helping to improve the patient’s field of vision.
- Skin Rejuvenation and Lifting:
Stimulating Collagen Production, Reducing Fine Wrinkles, and Firming the Skin One of the prominent applications of thermal plasma in dermatology is skin rejuvenation and lifting. The skin aging process, which involves the loss of collagen, elastin, and changes in skin structure, gradually leads to wrinkles and skin sagging. Thermal plasma, by generating controlled heat in various layers of the skin, stimulates the production of collagen and elastin, which helps strengthen and regenerate the skin.
When the electric arc from thermal plasma is applied to the skin, thermal energy is locally transferred and penetrates deeper skin layers. This process causes controlled microtrauma to the skin, which triggers collagen production and repairs damaged cells. The result of this process is firmer skin, reduced wrinkles, improved elasticity, and increased skin thickness.
This method is particularly effective for fine wrinkles around the eyes, forehead, cheeks, and mouth, with results typically achieved without the need for surgery, using only non-invasive treatments. Unlike traditional methods like CO2 laser, which require longer recovery times, treatment with thermal plasma has the shortest regeneration time, and patients can quickly return to their daily activities.
- Removal of Skin Lesions: Moles, Warts, and Other Superficial Lesions Precisely and Controlled
The removal of skin lesions such as moles, warts, seborrheic keratoses, and other superficial lesions is typically performed using surgical methods, lasers, or cryotherapy. However, the use of thermal plasma as a precise and controlled method for removing these lesions is rapidly gaining popularity.
Thermal plasma, by producing heat and electric arcs precisely at the targeted area, causes sublimation and removal of abnormal cells and damaged tissue without affecting the surrounding healthy tissue. This process is particularly more effective and safer than traditional methods like excision with a scalpel or laser in removing moles and warts. Thermal plasma transfers thermal energy to the skin, causing the damaged tissue to evaporate effectively, leaving no trace of the excess tissue.
One of the advantages of using thermal plasma in the removal of skin lesions is the high precision and ability to control the depth of energy penetration, allowing the practitioner to remove the lesion completely with minimal bleeding and without harming adjacent tissue. This method also helps reduce secondary infections and inflammation, as the tissue is removed with minimal damage and the risk of bleeding and infection is minimized.
As a result, the removal of lesions with thermal plasma is recognized as a safe and effective method compared to traditional approaches, offering fast and precise treatment with reduced recovery time, allowing the patient to return to their daily activities without the need for extended rest.
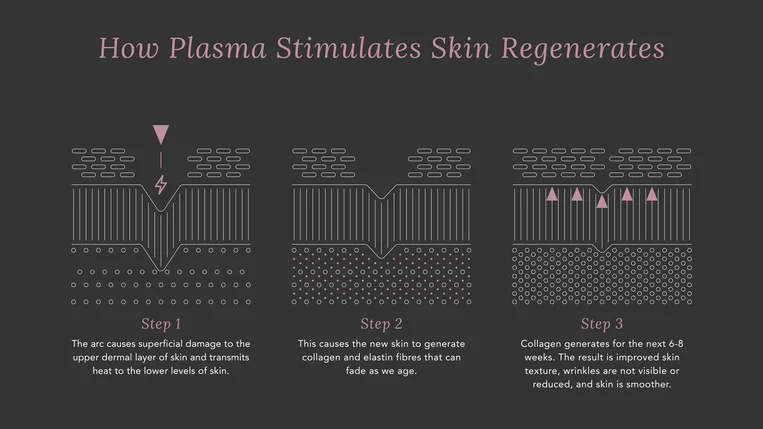
C. Fractional Plasma Technology: A New Generation of Plasma Therapy
Fractional plasma is an advanced and innovative technology that combines plasma technology with fractional techniques to provide precise, uniform, and non-invasive treatments for skin problems. This technology is especially effective in aesthetic and regenerative skin treatments, such as rejuvenation, wrinkle reduction, wound healing, and scar treatment. In this method, the energy produced by plasma is transferred in a controlled and targeted manner to both superficial and deeper layers of the skin.
Mechanism of Action of Fractional Plasma
Fractional plasma uses the generation of electric arcs and controlled heat on the skin’s surface to create a series of thermal microchannels in various layers of the skin. These microchannels directly enter the epidermal and dermal layers and cause minor damage to the affected tissues, stimulating the repair and regeneration process. These microscopic injuries activate cellular remodeling pathways and stimulate the production of collagen and elastin, which gradually leads to skin tightening and reduction of wrinkles.
One of the notable features of fractional plasma is that by creating thermal microchannels, energy is applied locally and focused on specific areas of the skin, allowing large areas to be treated simultaneously without transferring excessive energy to surrounding tissues. This feature is particularly effective for facial treatments and sensitive areas such as around the eyes and neck.
Benefits of Fractional Plasma in Skin Treatments
Reduced Treatment Time Fractional plasma, by dividing energy into smaller, more concentrated points, allows larger areas of the skin to be treated in a shorter amount of time. This feature reduces the number of treatment sessions and provides faster results. Compared to traditional methods that require longer sessions and invasive procedures, fractional plasma significantly reduces treatment time.
Increased Treatment Precision One of the most prominent features of fractional plasma is its ability to precisely control the depth of energy penetration into different layers of the skin. Using fractional techniques, the energy produced by plasma is targeted and focused on specific areas of the skin, effectively treating the affected regions while sparing the surrounding healthy tissue. This increases the treatment’s precision and minimizes the risk of side effects.
Uniform Energy Distribution and Non-invasive Treatment Fractional plasma divides energy into small and uniform areas, ensuring that energy is evenly distributed across the treatment zone. This results in uniform and natural treatment outcomes. Additionally, fractional plasma is recognized as a non-invasive method that does not require surgery or incisions and is performed without bleeding or pain. This is highly appealing to patients, as the recovery time is very short, and the side effects are minimal.
Prevention of Damage to Surrounding Tissues In fractional plasma treatments, energy is adjusted so that only the target areas of the skin are treated, and no excess energy is applied to surrounding healthy tissue. This feature minimizes damage to healthy tissue and ensures that the healing process is much faster and safer compared to invasive treatments. Moreover, this precise control of energy significantly reduces the risk of side effects such as thermal damage or burns.
Skin Regeneration and Improvement in Skin Quality The thermal microchannels created by fractional plasma activate skin regeneration and collagen rebuilding processes. This leads to skin that looks firmer, fresher, and younger. The production of collagen and elastin as a result of fractional plasma treatment helps strengthen the skin’s structure and reduces signs of aging such as wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging, giving the skin a younger and more refreshed appearance.
Application on Various Skin Types and Skin Lesions Fractional plasma is effective for a variety of skin types and can treat different skin lesions. This method can be used for treating fine wrinkles, acne scars, surgical wounds, pigmentation changes, and even stretch marks. Additionally, it is suitable for individuals with sensitive or damaged skin, as it can help repair the skin without causing severe inflammation or deep damage.

